Feature Engineering
Note
Before creating new feature research the domain and do some literature review
Handaling different data¶
Text Data¶
Text Processing¶
- Remove Html characters, punctuation
- Stop word removal
- Lower case conversion
- Stemming : Porter Stemmer, Snowball Stemmer
- Lemmitizatiom : break a sentence into word Ref1, Ref2
Text to Vectors¶
Bag of Words (BOW)¶
- Semantic meaning of word is lost
- Binary/Boolean BOW
- Count BOW
- Uni-gram/ Bi-gram/N-gram
TF-IDF Term Frequency Inverse Documents Frequency¶
Word2Vec¶
- Ways to train a Word2Vec Dictionary: CBOW & Skipgram
- CBOW predicts focus word given context words using an autoencoder model
- Skipgram predicts context word given focus word using an autoencoder model with multiple softmax (=number of context words) (Computationally more expensive to train, but can work with smaller data and infrequent words)
- Algorithmic optimisations for Skipgram and CBOW
- Hieraarchial Softmax - No of softmax needed = \(log_2(Vocab\ Size)\)
- Negatice Sampling - Update only a sample (based on frequency) of words including the target word
- In Word2Vec or Avg Word2Vec, Semantic information is learned by the vector
- References : Word Embedding | Tensorflow Reference | TFIDF Weighted Word2Vec
Positional Embedding¶
- Semantic and information about the Position in a sentence is captured
- Keras Position Embedding
- Transformers : Absolute Or Relative Positional Embedding
BERT & DistillBERT¶
- Can be used as replacement for word2vec
Note
Transformers are more efficient in parallel processing than LSTMs Reference 1, Reference 2
Categorical Data¶
- One hot encoding
- Mean value replacement or response coding
Time Series & Wave Form Data¶
Moving Window¶
- Within a Moving Window of width \(w\) calculate mean, std dev, median, quantiles, max, min, max - min, local minimas, local maximas, zero crossing
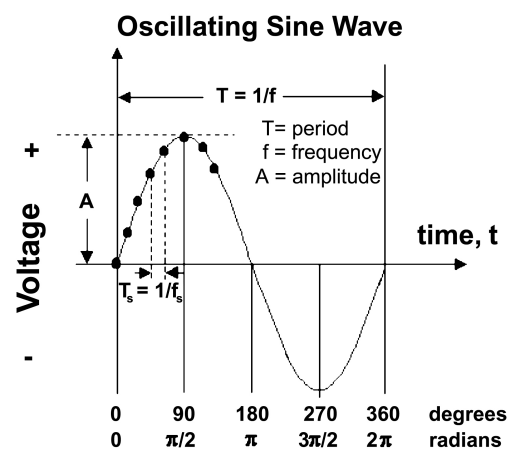
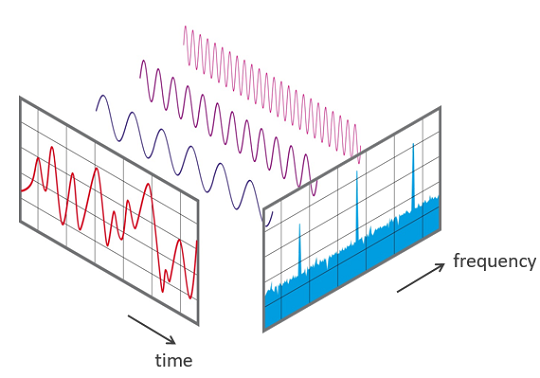
Fourier Transform¶
Any repeating pattern with Amplitude \(A\), Time Period \(T\), Frequency \(F\) and phase \(\phi\) can be broken down as sum of sine and cosines waves. Fourier Transform is used to convert a wave from Time domain to Frequency domain which is very insightful in repeating patterns
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)¶
- The input is a sequence of numbers of the original variable (one value per time step)
- The output is one value of amplitude (or signal strength) for each frequency. These are represented by the Fourier Coefficients.
- This new series is computed using the Fourier formula:
Now we obtain the frequencies that are present in the variable. Each of the values in the outcome series is the strength of a specific frequency. If the amplitude of a frequency is high, then that seasonality is important in the orginal time series (or waves). There exists an Computational optimized form of DFT called Fast Fourier Transform. It is computed using the Cooley-Tukey FFT algorithm.
Graph Data¶
Node Level Features¶
Node InDegree and Node OutDegree¶
Eigenvector Centrality¶
Clustering Coefficient¶
DeepWalk¶
Graph coloring¶
HOPE¶
Page Rank¶
Adar Index Kartz Centrality Shortest Path Connected-component HITS Score
Graph Level Features¶
Adjacency Matrix¶
Laplacian Matrix¶
Bag of Nodes¶
Weisfeiler-Lehman Kernel¶
Graphlet Kernels¶
Path-based Kernels¶
GraphHopper kernel, Neural Message Passing, Graph Convolutional Networks¶
Neighbourhood Overlap Features¶
Local Overlap Measures¶
Global Overlap Measures¶
¶
¶
¶
¶
Sequence Data¶
Image Data¶
- Colour Image Histogram - Tutorial
- Edge Histogams
- Haar Features
- SIFT Features : Very useful in Image Search with properties like scale invariance and rotation invariance
Graph Data¶
Feature Engineering¶
- Feature Binning and Indicator variables
- Depending on domain knowledge sometime it might be useful to convert real valued / categorical feature to bucketed/bined feature based on some rule
- To find the Binning thresholds / rule for a real valued variable \(X\) train a decision tree using \(X\) and target \(Y\) and get the threshold from the decision trees (trained on entropy)
- Interaction Variables :
- Logical \(N\) way Interaction between \(N\) variables created using Decision Trees of Depth \(N\)
- Numerical \(N\) way Interaction between \(N\) variables created using Mathamteical Operations between these features
- Feature Orthogonality : More orthogonal/different/uncorrelated features are better for learning a model
- Slicing Features : Features that help us divide the data into separate data generating process Eg: Device Feature : {Desktop, Mobile, Tablet} The way a customer would a product on mobile would be different and on computer would be different